A couple of times, you must have heard sound engineers mention ‘dynamic microphone,’ and a dynamic microphone basically talks about or refers to a dynamic moving coil microphone.
You can use these microphones for live stages, recording studios, and broadcasting, but how does a moving coil microphone work? What explanation sheds more light on a moving coil microphone? How important is this type of microphone?
If you have been struggling with finding answers to these questions mentioned above, you need to stop looking for answers, as we will explain in detail in this post. The first we want to address is what a moving coil microphone is.
Content Navigation
What Is A Dynamic Microphone
A dynamic microphone is considered a moving coil microphone that uses a transducer designed to convert sound waves into microphone signals using electromagnetic induction.
A conductive coil attached to the diaphragm will move when the diaphragm moves, and this conductive coil will oscillate inside a magnetic field.
This movement brings about an alternating current voltage across the coil, and this AC voltage is sent out as a signal from the microphone. Now, you know what a dynamic moving coil microphone is, but you might also be puzzled about the origin of the name.
So many people think that dynamic microphones possess a dynamic build or dynamic features compared to condenser microphones. This might be true when you say a dynamic microphone has a dynamic range over a condenser microphone, but this is the reason behind the name, ‘dynamic microphone.’
Moving From Dynamo To Dynamic Microphone
Truly, dynamic microphones are more dynamic than condenser microphones because of maximum sound pressure levels and no self-noise design. However, they got the name dynamic microphone from their predecessor Dynamo.
This brings us to the question, what is a dynamo? Like every other microphone, Dynamo microphones act like transducers in converting mechanical energy into electrical energy using electromagnetic induction.
Dynamo microphones function by rotating wire coils inside an electromagnetic field. Dynamo microphones are known to produce direct current, while its audio signal is its alternating current.
Even though dynamic microphones were designed based on a dynamo microphone’s principle, they have not considered dynamo microphones.
A dynamic microphone’s coil of wire moves in the front and back direction of a magnetic field, and inducing alternating currents across the coil of wire is what this movement generates. Technically, small ‘AC dynamos’ that are present in a dynamic microphone are called magnetos.
Meaning Of ‘Moving Coil’
Every moving coil microphone is considered a dynamic microphone, and this is because they are transducers that make use of the electromagnetic induction principle to function. However, a very crucial point you should note is not every dynamic microphone possesses a moving coil.
The famous ribbon microphone is also classified as a dynamic microphone, so the ‘moving coil’ term separates the dynamic microphones that have moving coils and the ones that don’t have them.
How Does A Moving Coil Microphone Work
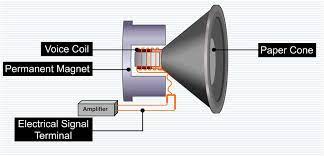
The moving coil microphone is more popular than the ribbon-type microphone, which explains why the term dynamic microphone is used to describe them all. However, instead of using dynamic ribbon microphones, it is okay to call them to ribbon microphones.
The Conductor (Moving Coil)
Not everyone has an idea what an electrical conductor is, but electrical conductors are any objects that permit the flow of electricity through them in any direction. For example, a dynamic microphone’s moving coil is tightly wound.
This coil has a small diameter of a conductive wire, making it look like a tiny ring. This coil works by moving with the diaphragm inside an electromagnetic field, and it is designed to be part of a closed circuit.
The moving coil is considered one of the most vital components of a two-key transducer. This moving coil will transform mechanical energy to electrical energy using the help of a magnet. Still, the material that makes up the moving coil might be a little bit difficult to identify.
Interesting, moving coils are made using flexible materials, and this material tends to be copper most of the time. Moving coils are typically made up of small diameter copper wires, which get wound several times around.
Copper is one of the best materials used in making a moving coil, not because of its price alone but because it supports electromagnetic induction.
Copper is also known for producing strong audio signals, and properly positioning a moving coil inside a microphone is essential. Just like we mentioned earlier, a moving coil is attached to a diaphragm’s groove, and it won’t come in contact with anything apart from the diaphragm.
This coil is suspended inside the gap of a microphone’s capsule, and the gap is a ring of space that features a magnetic structure.
Despite this copper wire having a minimal diameter, it still gets wound a couple of times in the overall coil. This produces about three benefits mentioned below;
- Since the magnetic gap is smaller, it will be easy to concentrate the magnetic field around the coil.
- It is possible to have a longer wire length inside the same coil, which helps boost conductivity.
- There will be an increase in the number of conductors that can cut through magnetic fields because more loops inside the coil.
Why Are Two Signal Wires Taken From A Moving Coil
You will need more than just a conductive coil and magnetic field for the electromagnetic inductor to take place fully. A closed circuit is also needed, and this circuit will involve a coil of wires. For example, two signal wires are always attached to the moving coil of a dynamic microphone, and they are attached at one end each of the tightly wound copper.
These two signal wires are connected to the transformer to allow electromagnetic induction while the electrical circuit stays closed.
Wrapping It Up – How Does A Moving Coil Microphone Work
We have come to the end of this interesting post, and we hope that you find this post helpful and answer all of your questions. We will appreciate reading all of your comments in the comment section.
Related Posts
How To Sight Read For Beginners
Speaker Distortion At High Volume

